Food Processor and a Blender: 10 Essential Differences You Need to Know

When it comes to modern kitchen appliances, two of the most versatile and commonly used tools are the food processor and the blender. Both are invaluable for a variety of food preparation tasks, yet they each excel in different areas and are designed for specific purposes. Understanding the distinctions between a food processor and a blender can help you choose the right appliance for your cooking needs, whether you’re chopping vegetables, kneading dough, or whipping up a smoothie. In this article, we’ll explore the key differences between these two appliances, their primary uses, and how they can enhance your culinary experience.
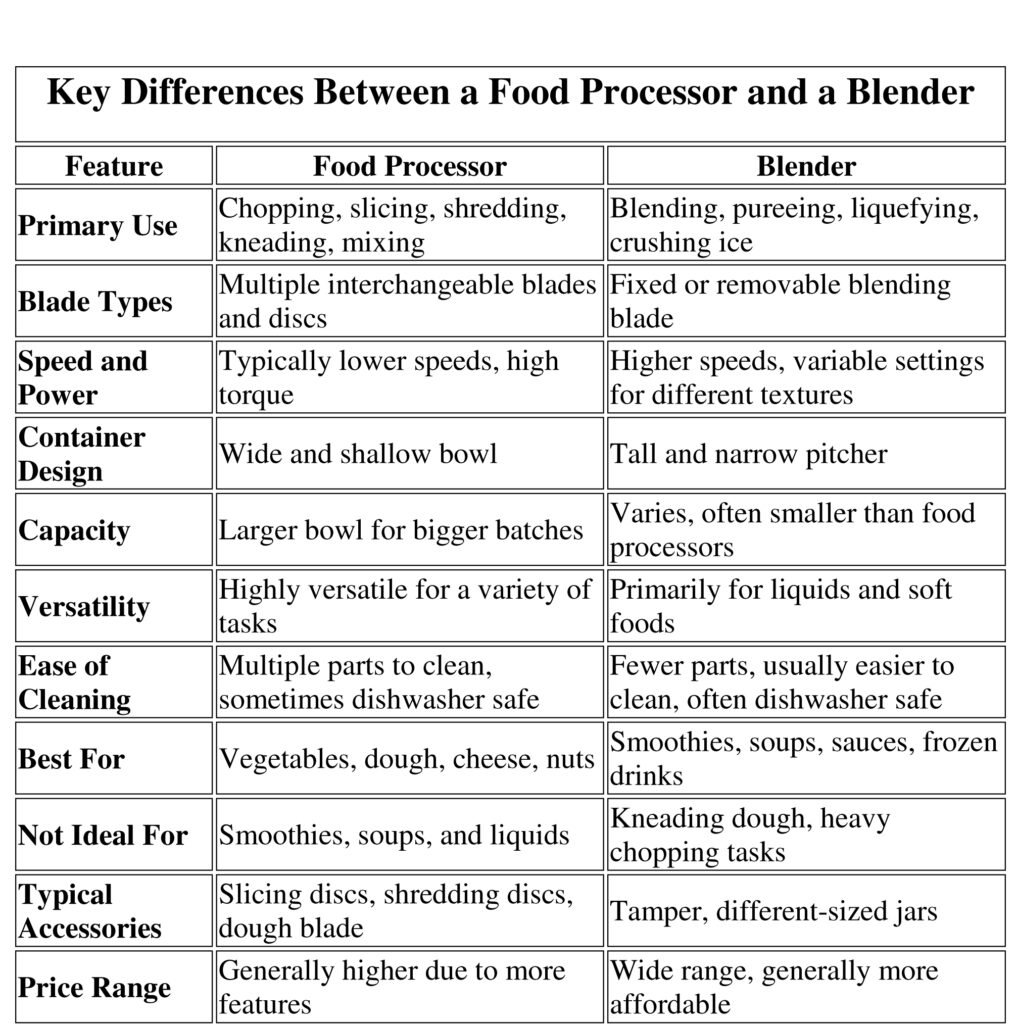
Detailed Comparison:
- Primary Use:
Food Processor: It is a versatile tool primarily used for chopping, slicing, grating, and shredding. Its powerful motor and various attachments make it ideal for tasks such as chopping vegetables, making dough, grating cheese, and slicing fruits. The food processor’s broad, flat blade is perfect for creating even cuts and maintaining the texture of ingredients. Additionally, it excels at pureeing ingredients without adding extra liquid, making it suitable for preparing dips like hummus, spreads, and thick sauces.
Blender: On the other hand, a blender is primarily used for tasks requiring a smooth, liquid consistency. Its design, featuring a narrow, tall jar and sharp, high-speed blades, is perfect for blending liquids and softer ingredients. The blender shines in making smoothies, milkshakes, soups, and sauces that require a consistent, homogeneous texture. It efficiently blends fruits, vegetables, and liquids, creating a smooth and drinkable mixture Blenders can crush ice, making them perfect for preparing frozen drinks and cocktails.
- Blade Types:
Food Processor: Comes with multiple interchangeable blades and discs designed for specific tasks such as slicing, shredding, and chopping.
Blender: Usually has a fixed blade, optimized for creating smooth textures by blending ingredients.
- Speed and Power:
Food Processor: Operates at lower speeds with high torque, making it suitable for tougher tasks like kneading dough.
Blender: Features higher speeds and variable settings to achieve the desired consistency for liquids and purees.
- Container Design:
Food Processor: Features a wide and shallow bowl that allows for easier addition and processing of solid ingredients.
Blender: Equipped with a tall and narrow pitcher that helps create a vortex to blend liquids and soft foods efficiently.
- Capacity:
Food Processor: Typically has a larger bowl capacity, suitable for processing bigger batches of ingredients at once.
Blender: Often has a smaller capacity, but high-performance models can handle larger volumes.
- Versatility:
Food Processor: Extremely versatile, capable of handling a wide range of food preparation tasks.
Blender: While primarily used for liquids, some high-powered blenders can perform additional tasks like making nut butter.
- Ease of Cleaning:
Food Processor: Can be more challenging to clean due to multiple parts, but many components are dishwasher safe.
Blender: Generally easier to clean with fewer parts; most models have dishwasher-safe components.
- Best For:
Food Processor: Best suited for tasks that involve solid ingredients, such as chopping vegetables, slicing fruits, and kneading dough.
Blender: Ideal for blending liquids, making smoothies, pureeing soups, and crushing ice for frozen drinks.
- Not Ideal For:
Food Processor: Not well-suited for making smoothies or other tasks involving a high volume of liquids.
Blender: Not designed for heavy chopping, slicing, or kneading dough.
- Typical Accessories:
Food Processor: Often comes with a variety of attachments such as slicing discs, shredding discs, and a dough blade.
Blender: May include accessories like a tamper to push ingredients down and different-sized jars for various blending tasks.
- Price Range:
Food Processor: Generally more expensive due to its versatility and range of features.
Blender: Offers a wide price range, with basic models being more affordable and high-performance models costing more.
Conclusion:
Choosing between a food processor and a blender depends on your specific needs in the kitchen. If you frequently prepare a variety of ingredients and need a versatile tool, a food processor may be the better choice. If your primary focus is on making smoothies, soups, and other liquid-based recipes, a blender will likely suit your needs better.